National Thyroid Awareness Month
![]()
January is National Thyroid Awareness Month; we’d like to join in by recognizing this national event by educating about thyroid health. Read below to learn about what the thyroid is, get informed about thyroid disease, how diabetes and thyroid disease are related, and symptoms and methods of prevention for thyroid disease.
What is the Thyroid?
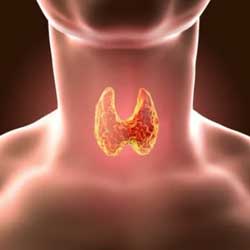 The thyroid gland is a small organ located in the front of the neck. Like other glands in your body, the thyroid produces chemical substances to support body functions.
The thyroid gland is a small organ located in the front of the neck. Like other glands in your body, the thyroid produces chemical substances to support body functions.
The thyroid produces thyroid hormones including triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4), that have a great impact on your body’s vital functions and supports all aspects of your metabolism.
What is Thyroid Disease?
When your thyroid is not working properly, it can affect your whole body.
There are two main thyroid diseases, Hyperthyroidism, and Hypothyroidism. Another common thyroid disease is Hashimoto’s Disease, which is a condition in which your immune system attacks your thyroid.
The cause of these diseases can come from a variety of conditions. Families who have a history of thyroid disease are more at risk than those without a history.
Hyperthyroidism is when your thyroid produces too many thyroid hormones and your body uses energy too quickly. This results in feeling overly tired, losing weight, anxiety, and an increased heart rate.
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid produces too few hormones. This can result in feeling fatigue, weight gain, and possibly have a hard time tolerating low temperatures.
Thyroid Disease and Diabetes
There is a higher risk for those with Type I and Type II diabetes to develop a thyroid disease
Type I Diabetes: Those who have Type I diabetes, or any other autoimmune disorder are at higher risk for developing thyroid disease. It is recommended that if you have Type I Diabetes that you should test often for thyroid disease.
Type II Diabetes: The risk of developing a thyroid disease is lower with Type II Diabetes compared to those who have Type I Diabetes, however the risk of developing a thyroid disease is higher than those who have no Diabetes. This is because of the relationship they share with the metabolism, and the regulation of blood sugar.
How You can Support Your Thyroid
Luckily, there are many natural ways you can support your thyroid health, including adjusting your diet.
- Iodine: Having a deficiency in iodine can also be a factor in your thyroid health; Because Iodine is the building block of thyroid hormone. Iodine is common in foods such as dairy, seafood, and iodated table salt which should be consumed in moderation.
- Vitamins and Supplements: Vitamins and supplements can not only help maintain your thyroid hormone production, but also support your immune system to avoid Hashimoto’s disease.Incorporating Zinc into your diet may enhance your thyroid’s hormone production.Your immune system is crucial to your thyroid’s ability in combating Hashimoto’s disease. You can support your immune system with vitamins and supplements such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Vitamin C, and Magnesium.
- Diet: Avoid intake of processed foods that include refined sugars, preservatives, and dyes. Instead look for foods that are rich in antioxidants, (Click here for our list of foods that are high in antioxidants.), probiotics, and heart-healthy fats such as cold pressed extra virgin olive oil, flax seed oil, avocado oil, and sunflower oil.
If you’re not sure where to start with adjusting your diet, or have questions about your thyroid health, talk to your doctor, contact us to schedule an appointment.
– The ProNatural Wellness Team












